Imagine standing on the deck of a massive vessel, the icy sea spray mingling with the crisp air, destined for ports that rely heavily on liquefied natural gas. There’s a fascinating yet complex world of LNG carriers that unfolds, where intricate design meets critical safety protocols. For those unfamiliar, navigating these waters can initially seem daunting, but this guide aims to unravel the layers of LNG cargo operations, especially for those gearing up for oral exams within the maritime field.
What Are LNG Carriers? Understanding Their Role
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) carriers are specialized vessels designed to transport LNG across the globe. But what exactly are they, and why are they so important in the energy sector? Let's dive into the world of LNG carriers and explore their significance in energy transportation.
Definition and Importance of LNG Carriers
LNG carriers are essential for moving liquefied natural gas to various global markets. They play a crucial role, especially in regions like Asia, where demand for cleaner energy sources is skyrocketing. LNG is considered a cleaner alternative to traditional fossil fuels, making these carriers vital for the energy transition.
Why is LNG so important? As countries strive to reduce their carbon footprints, LNG offers a viable solution. It emits less carbon dioxide when burned compared to coal or oil. Thus, LNG carriers are not just vessels; they are the backbone of our energy transition, safely transporting the future of clean energy.
Key Features of LNG Carriers
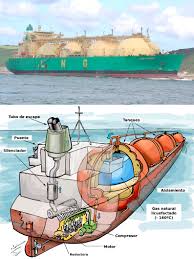
One of the standout features of LNG carriers is their double-hulled design. This design is crucial for safety and efficiency. The double hull provides an additional layer of protection, reducing the risk of leaks and spills during transportation. This is particularly important given the hazardous nature of LNG.
Another key feature is cryogenic technology. LNG must be kept at extremely low temperatures, around minus 160 degrees Celsius, to remain in liquid form. This requires specialized insulation and handling systems. The cryogenic nature of LNG means that it occupies only one-sixth of its gaseous volume when liquefied. This efficiency makes it an advantageous fuel option compared to petroleum.
Comparison to Traditional Oil Tankers
When comparing LNG carriers to traditional oil tankers, several differences emerge. Traditional oil tankers are designed to transport crude oil and refined products. They do not require the same level of insulation or temperature control as LNG carriers. This makes LNG carriers more complex in design and operation.
- Safety Features: LNG carriers have enhanced safety measures due to the flammable nature of LNG.
- Operational Complexity: LNG carriers involve intricate loading and unloading processes, including managing boil-off gas and maintaining tank pressure.
- Environmental Impact: LNG carriers contribute to lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to oil tankers.
In essence, while both types of vessels serve critical roles in energy transportation, LNG carriers are at the forefront of the shift towards cleaner energy solutions.
Growth in LNG Demand and Its Implications
The demand for LNG is growing rapidly, particularly in Asia. Current estimates suggest that LNG demand in this region is increasing at an impressive rate of 10% annually. This surge is driven by the need for cleaner energy sources and the expansion of natural gas infrastructure.
What does this mean for LNG carriers? As demand rises, so does the need for more carriers. This presents both opportunities and challenges. On one hand, increased demand can lead to economic growth and job creation in the maritime and energy sectors. On the other hand, it necessitates advancements in technology and safety measures to ensure the safe transport of LNG.
Moreover, the growth in LNG demand has implications for global energy markets. Countries that invest in LNG infrastructure may find themselves in a stronger position in the international energy landscape. This shift could redefine energy trade routes and influence geopolitical relationships.
Conclusion
In summary, LNG carriers are more than just ships; they are vital components of the global energy supply chain. Their unique features, such as double-hulled designs and cryogenic technology, enable them to transport LNG safely and efficiently. As demand for LNG continues to rise, these carriers will play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of energy transportation.
"LNG carriers are the backbone of our energy transition, safely transporting the future of clean energy." - Energy Expert

The Science Behind LNG: Cryogenics and Composition
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) is a fascinating subject, especially when delving into its science. Understanding the processes that transform natural gas into a liquid form is crucial. This transformation is not just a simple task; it involves intricate methods and specialized knowledge. Let's explore the liquefaction process, the chemical composition of LNG, and the importance of cryogenic temperatures.
1. The Liquefaction Process
The liquefaction of natural gas is a critical step in the production of LNG. This process involves cooling the gas to approximately -160°C. Why such a low temperature? At this point, natural gas condenses into a liquid, reducing its volume to about one-sixth of its gaseous state. This significant reduction makes LNG a more efficient fuel option for transportation and storage.
To achieve these extreme temperatures, specialized equipment is necessary. The liquefaction process typically involves several stages:
- Pre-treatment: This stage removes impurities such as water, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen sulfide. These components can cause problems during the liquefaction process.
- Cooling: The gas is then cooled using various refrigeration cycles. These cycles utilize different refrigerants to achieve the desired temperature.
- Storage: Once liquefied, LNG is stored in double-hulled tanks designed to maintain the low temperatures required.
Each step in this process is vital. Any miscalculation can lead to inefficiencies or even dangerous situations. As an LNG specialist once said,
"Understanding the science of LNG is crucial for any maritime professional in this field."
2. Chemical Composition of LNG
Now, let’s discuss what LNG is made of. The primary component of LNG is methane (CH4), which constitutes about 85% of its composition. The remaining 15% includes other hydrocarbons:
- 10% Ethane
- 5% Other hydrocarbons (like propane and butane)
This composition is crucial for understanding LNG's properties and behavior. Methane is a clean-burning fuel, making LNG an attractive energy source, especially in regions looking to reduce emissions.
Moreover, the liquefaction process ensures that undesirable components are removed. This is essential for maintaining the quality and safety of LNG during transport. The removal of water and other impurities prevents issues like freezing or corrosion in pipelines and storage tanks.
3. Importance of Cryogenic Temperatures
The significance of cryogenic temperatures in LNG cannot be overstated. At -160°C, LNG remains in a liquid state, which is vital for safe and efficient transportation. But why is this temperature so important?
First, maintaining LNG at cryogenic temperatures ensures that it remains stable. If the temperature rises, LNG can vaporize, leading to increased pressure in storage tanks. This can create hazardous situations, including leaks or explosions.
Additionally, the design of LNG carriers and storage facilities must accommodate these low temperatures. Materials used in construction must be able to withstand thermal stress and prevent heat transfer. This is why LNG carriers often feature double-hulled designs, which provide insulation and safety.
In summary, the science behind LNG involves a complex interplay of processes and properties. The liquefaction process, the chemical composition, and the importance of maintaining cryogenic temperatures all contribute to the safe and efficient use of LNG as an energy source. As the demand for cleaner energy continues to grow, understanding these elements becomes increasingly crucial.

Navigating Safety Protocols in LNG Operations
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) operations are not just about transporting a fuel source; they involve a complex web of safety protocols. The hazardous nature of LNG requires a keen focus on safety at every stage of operation. This section delves into the responsibilities of crew members aboard LNG carriers, the critical processes of inerting operations, and the emergency protocols in place for potential LNG leakage.
1. Analysis of Crew Responsibilities Aboard LNG Carriers
The crew aboard LNG carriers plays a vital role in ensuring safe operations. Their responsibilities are multifaceted and require extensive training. Here are some key duties:
- Loading and Unloading: Crew members must manage the loading and unloading of LNG with precision. This involves coordinating with terminal operators and ensuring that all safety measures are in place.
- Monitoring Systems: The cargo control room is equipped with advanced monitoring systems. Crew members must constantly check these systems to ensure everything is functioning correctly.
- Safety Checks: Regular safety checks are essential. Crew members must ensure that all equipment is in good working order and that safety protocols are being followed.
- Emergency Preparedness: Crew members must be trained to respond to emergencies. This includes knowing evacuation routes and emergency procedures.
In the LNG industry, safety isn’t just a guideline but a culture we live by. This ethos is instilled in every crew member through rigorous training and adherence to safety standards.
2. Inerting Operations: Importance and Procedures
Inerting operations are crucial for maintaining safety during LNG operations. But what exactly does inerting mean? In simple terms, it involves replacing the air in the cargo tanks with an inert gas, typically nitrogen. This process is essential for preventing explosions and ensuring a safe environment for crew members.
Here’s how the inerting process typically unfolds:
- Preparation: Before any maintenance or loading operations, the tanks must be inerted. This involves monitoring oxygen levels and ensuring they are below a certain threshold.
- Gas Generation: Nitrogen is generated on board and distributed throughout the cargo tanks. This step is critical to ensure that no flammable mixtures are present.
- Continuous Monitoring: Throughout the inerting process, crew members must continuously monitor pressure and oxygen levels. This ensures that the tanks remain in a non-flammable state.
By following these procedures, the crew can significantly reduce the risk of fire or explosion during operations. The importance of inerting cannot be overstated; it is a fundamental aspect of LNG safety protocols.
3. Emergency Protocols for LNG Leakage
Despite the best precautions, emergencies can still occur. LNG leakage is one of the most critical risks in LNG operations. Therefore, having robust emergency protocols is essential.
Here are the key components of emergency protocols for LNG leakage:
- Immediate Response: Upon detecting a leak, crew members must act quickly. This includes shutting down operations and alerting the necessary authorities.
- Evacuation Procedures: Crew members must know the evacuation routes and procedures. This ensures that everyone can exit the vessel safely and efficiently.
- Containment Measures: If possible, crew members should implement containment measures to prevent the spread of LNG. This may involve using barriers or other equipment.
- Communication: Clear communication is vital during an emergency. Crew members must keep in contact with each other and with emergency services.
Training is essential for crew members to respond effectively to LNG leaks. Regular drills and simulations help ensure that everyone knows their role in an emergency.
In conclusion, navigating safety protocols in LNG operations is a complex but crucial task. The responsibilities of the crew, the importance of inerting operations, and the protocols for handling emergencies all play a significant role in ensuring safety. With the right training and adherence to safety standards, the risks associated with LNG operations can be effectively managed.

The Cargo Loading and Unloading Process: Efficiency and Precision
The loading and unloading of liquefied natural gas (LNG) is a complex dance. It requires precision and coordination. Every step must be executed flawlessly to ensure safety and efficiency. But what does this process entail? Let's break it down.
Step-by-Step Procedures for Cargo Operations
Understanding the cargo operations of LNG carriers involves several key steps:
- Preparation: Before loading begins, the LNG carrier must be cooled down. This is crucial to maintain the low temperatures necessary for LNG, which is around minus 160 degrees Celsius.
- Inerting: The cargo tanks are filled with inert gas, often nitrogen, to prevent any flammable mixtures. This step is vital for safety.
- Loading: The LNG is pumped from the terminal into the carrier’s tanks. This process must be closely monitored to ensure that the pressure remains within safe limits.
- Transport: Once loaded, the LNG carrier sets sail. During transit, the crew must manage boil-off gas, which is the gas that evaporates from the LNG due to temperature changes.
- Unloading: Upon arrival at the destination terminal, the LNG is unloaded. This involves reversing the loading process, ensuring that the pressure is managed effectively.
- Post-Operation: After unloading, the tanks are cleaned and prepared for the next operation.
Each of these steps requires meticulous attention to detail. The crew must work in harmony with terminal operators to ensure everything runs smoothly. As a shipping analyst once said,
"The choreography of cargo operations is crucial for seamless LNG transportation."
Roles of Terminal and LNG Carriers During Loading/Unloading
Both terminal operators and LNG carriers play pivotal roles in the loading and unloading process. Their responsibilities are distinct yet intertwined:
- Terminal Operators: They manage the loading facilities, ensuring that all equipment is functioning correctly. They also monitor the flow of LNG and maintain communication with the carrier.
- LNG Carriers: The crew on board the LNG carriers is responsible for the safe handling of the cargo. They must ensure that the tanks are properly cooled and that the inerting process is completed before loading begins.
This collaboration is essential. If one side falters, it can lead to delays or, worse, safety hazards. Coordination is key. Without it, the entire operation could be compromised.
Importance of Pressure Management and Vapor Return Systems
Pressure management is a critical aspect of LNG operations. The cargo tanks must maintain specific pressure levels to prevent leaks and ensure safety. Here’s why:
- Preventing Leaks: If the pressure is too high, it can lead to dangerous situations, including potential leaks. This is where vapor return systems come into play.
- Vapor Return Systems: These systems help manage the pressure within the tanks by returning vaporized LNG back to the terminal. This process not only maintains safety but also improves efficiency.
- Efficiency Rates: Studies show that effective vapor return systems can significantly reduce the amount of boil-off gas, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
In essence, managing pressure and utilizing vapor return systems are not just operational tasks; they are vital for the safety and reliability of LNG transportation.
Conclusion
The cargo loading and unloading process for LNG carriers is intricate and requires a high level of coordination. From the step-by-step procedures to the roles of terminal operators and LNG carriers, every detail matters. Pressure management and vapor return systems are crucial for maintaining safety and efficiency. Understanding these elements can help demystify the complexities involved in LNG operations.

Challenges and Innovations in LNG Carrier Design
The world of liquefied natural gas (LNG) transportation is evolving rapidly. As demand for cleaner energy sources grows, innovations in LNG carrier design are becoming crucial. But with these innovations come significant challenges. This section explores both the advancements and the hurdles faced by the industry.
Current Innovations in LNG Carrier Design
Innovation is at the heart of modern LNG carrier design. These vessels are not just ships; they are engineering marvels. Here are some key innovations:
- Double-hulled designs: This feature enhances safety by providing an additional layer of protection against leaks.
- Advanced insulation materials: These materials help maintain the extremely low temperatures required for LNG, which is about minus 160 degrees Celsius.
- Improved cargo containment systems: Innovations in tank design, such as spherical and prismatic shapes, optimize space and safety.
- Energy-efficient propulsion systems: New technologies are being developed to reduce fuel consumption and emissions during transit.
These advancements are not just about efficiency; they also focus on safety. As one maritime engineer aptly stated,
“Innovation in LNG carrier design is vital for a sustainable future in energy transport.”This sentiment underscores the importance of continuous improvement in design standards.
Challenges Facing the Industry: Climate Impact and Regulation
Despite the innovations, the LNG industry faces several challenges. One of the most pressing issues is the impact of climate regulations. As governments worldwide tighten regulations on emissions, LNG carriers must adapt. The specifications for these vessels are changing, and they must now comply with stricter environmental standards.
Here are some challenges the industry is grappling with:
- Regulatory compliance: Meeting new environmental standards can be costly and complex.
- Carbon footprint reduction: The industry is under pressure to minimize its environmental impact.
- Public perception: As awareness of climate change grows, public scrutiny of fossil fuel transportation increases.
These challenges require innovative solutions. For instance, some companies are exploring carbon capture technologies to reduce emissions from LNG carriers. The goal is to make LNG a more sustainable energy source while addressing environmental concerns.
Future Trends in LNG Transportation
Looking ahead, several trends are shaping the future of LNG transportation. The industry is poised for growth, with projected increases in LNG shipping capacity expected in the coming years. This growth is driven by rising demand in emerging markets, particularly in Asia.
Key trends include:
- Increased automation: Automation in loading and unloading processes is expected to enhance safety and efficiency.
- Digitalization: The use of digital technologies for monitoring and managing LNG operations is on the rise.
- Focus on sustainability: Future designs will likely prioritize eco-friendly materials and technologies to reduce the carbon footprint.
As the industry evolves, the integration of these trends will be essential. The forward-looking perspective on LNG carrier designs addresses both opportunities and challenges. Companies that embrace innovation while navigating regulatory landscapes will likely lead the way.
In summary, the LNG carrier design landscape is undergoing significant transformation. Innovations are paving the way for safer, more efficient vessels. However, the industry must also confront the challenges posed by climate regulations and public perception. The future of LNG transportation looks promising, with trends indicating a shift towards more sustainable practices. As the industry adapts, it will be fascinating to see how these changes unfold.
The Economic and Environmental Impact of LNG Transportation
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) has emerged as a significant player in the global energy market. As a clean energy alternative to petroleum, it offers various advantages that are hard to ignore. But what exactly makes LNG so appealing? Let's delve into its economic implications and environmental benefits.
LNG as a Clean Energy Alternative
LNG is primarily composed of methane, a cleaner-burning fossil fuel. When compared to petroleum, LNG produces significantly lower carbon emissions. This reduction is crucial in the fight against climate change. In fact, studies show that using LNG instead of petroleum can lead to a reduction in CO2 emissions by up to 30%. That's a substantial figure, isn't it?
Moreover, LNG occupies about one-sixth of its gaseous volume when liquefied. This property makes it easier to transport over long distances. As countries strive to meet their energy needs, LNG provides a viable solution. It is especially beneficial for rapidly developing markets in Asia and Southeast Asia, where energy demands are soaring.
Economic Implications for Exporting and Importing Nations
The economic dynamics surrounding LNG are fascinating. For exporting nations, LNG represents a lucrative opportunity. Countries rich in natural gas can capitalize on global demand. This can lead to increased revenues and economic growth. For instance, the LNG market value is projected to reach billions of USD in 2023. This figure highlights the growing importance of LNG in the global energy landscape.
- Exporting Nations: They can boost their economies by tapping into the LNG market.
- Importing Nations: They benefit from a diversified energy supply, reducing dependence on a single source.
However, the economic implications extend beyond mere profits. The price of LNG can significantly affect global energy prices. When demand surges, prices can rise, impacting consumers worldwide. This interconnectedness raises questions about energy security and market stability. Are we prepared for the fluctuations that come with this dependence on LNG?
Environmental Benefits of LNG
One of the most compelling arguments for LNG lies in its environmental benefits. As mentioned earlier, LNG can significantly reduce carbon emissions compared to petroleum. This is not just an economic shift; it’s an environmental imperative for our planet. As stated by an Energy Economist,
“The shift to LNG is not just economic; it’s an environmental imperative for our planet.”
In addition to lower emissions, LNG also produces fewer pollutants. This means cleaner air and a healthier environment. For countries grappling with air quality issues, LNG offers a way to transition towards cleaner energy sources. It plays a pivotal role in the energy transition, especially in rapidly developing markets. But the benefits don't stop there.
Switching to LNG can also help countries meet their climate goals. Many nations are committing to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. LNG can be a stepping stone towards achieving these targets. It provides a bridge to a more sustainable energy future. But is it enough? Can LNG truly replace more harmful energy sources in the long run?
Conclusion
In summary, the economic and environmental dimensions of LNG highlight its significance in the energy landscape. As countries navigate the complexities of energy demands, LNG stands out as a clean alternative to petroleum. Its economic implications for exporting and importing nations are profound, while its environmental benefits cannot be overlooked. The future of energy may very well depend on how we embrace LNG in the coming years.
Conclusion: The Future of LNG Carriers and Global Energy Supply
The significance of LNG carriers cannot be overstated. These specialized vessels are essential for transporting liquefied natural gas, a clean and efficient energy source. As the world shifts towards more sustainable energy solutions, LNG plays a pivotal role in this transition. The demand for LNG is rising, particularly in rapidly growing economies in Asia and Southeast Asia. This trend highlights the importance of LNG carriers in ensuring a reliable energy supply.
The Role of LNG in the Global Energy Transition
LNG serves as a bridge in the global energy transition. It is a cleaner alternative to traditional fossil fuels, emitting less carbon dioxide when burned. As countries strive to meet their climate goals, LNG is becoming a preferred choice. It provides a stable energy source while reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This transition is not just about switching fuels; it’s about rethinking how energy is produced and consumed.
Consider this: as the world moves away from coal and oil, LNG offers a viable solution. It can support renewable energy sources like wind and solar by providing backup power when these sources are not available. This flexibility makes LNG a crucial component in the energy mix of the future.
Future Outlook for LNG Shipping and Technology Advancements
The future of LNG shipping looks promising. With advancements in technology, LNG carriers are becoming more efficient and safer. Innovations in ship design, such as double-hulled structures, enhance safety during transportation. These designs help maintain the low temperatures required for LNG, which is crucial for preventing evaporation and ensuring safe handling.
Moreover, the industry is witnessing significant investment trends in LNG technology. Companies are focusing on developing more efficient engines and cargo handling systems. These improvements not only enhance operational efficiency but also reduce the environmental impact of LNG shipping. As one industry leader aptly stated,
"LNG carriers will lead the charge into a cleaner energy future."
However, the shipping industry must adapt to these changes. As demand for LNG rises, there is a pressing need to implement new technologies and safety protocols. The ongoing challenge remains balancing economic benefits with environmental responsibilities. It’s a delicate dance, but one that the industry is committed to navigating.
Projected Growth Rates and Investment Trends
Looking ahead, the projected growth rates for LNG demand globally are encouraging. Analysts predict that as more countries adopt LNG as a primary energy source, the market will continue to expand. This growth will likely drive further investments in LNG infrastructure, including terminals and shipping fleets. The investment trends indicate a robust future for LNG technology, which will be crucial in meeting the rising demand.
In summary, LNG carriers are not just vessels; they are vital components of the global energy supply chain. Their importance will only grow as the world seeks cleaner energy solutions. The role of LNG in the energy transition is clear, and the future of LNG shipping is bright with advancements in technology and safety. The industry stands at a crossroads, ready to embrace the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
As the world continues to evolve, LNG carriers will play an integral role in shaping the future of energy. The commitment to safety, efficiency, and sustainability will guide the industry as it navigates this new landscape. With LNG at the forefront, the journey towards a cleaner energy future is just beginning.
TL;DR: This post provides a detailed overview of LNG carriers, covering their operational intricacies, safety measures, and the significant role LNG plays as a clean energy source globally.
Comments
Post a Comment