As a kid, the closest I got to the open ocean was poking at tide pools in rubber boots. Little did I know that half a world away, ginormous ships were gliding across the sea, their engines running like clockwork. The real secret? Not magic, not luck, not even duct tape—just rigorously planned maintenance, humming quietly below deck. Think of it as the ultimate life hack for ships, one that has quietly transformed safety, economics, and even the resale value of a vessel. Let's journey from chaos to control and see how PMS quietly props up an entire industry.
From Firefighting to Foresight: The Evolution of Ship Maintenance
Imagine a massive cargo ship, far from any port, carrying goods vital to the global economy. What keeps its intricate machinery running day after day, avoiding disaster? Decades ago, the answer was simple—wait for something to break, then scramble to fix it. This “firefighting” approach defined early ship maintenance: panic, fix, repeat. The risks were enormous. As one industry expert put it,
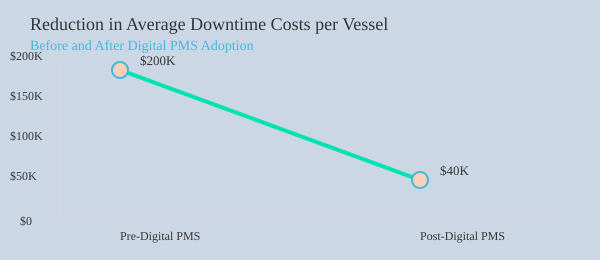
“An unplanned engine failure on a big container ship could cost the company upwards of two hundred thousand a day.”
Historically, maintenance was reactive. Crews relied on paper logs and checklists, mainly to satisfy inspectors, not to prevent failures. This system offered little real progress. The unpredictable nature of breakdowns led to massive repair bills, operational delays, and, most importantly, safety risks for both crew and cargo. As ships became more complex, this approach simply couldn’t keep up.
The turning point came with the adoption of digital Planned Maintenance Systems (PMS). These platforms transformed ship maintenance from chaotic, last-minute fixes to coordinated, risk-managed processes. Digital PMS platforms now integrate inventory, scheduling, and compliance, giving ship operators a clear, real-time view of every critical system. This shift has been fundamental for cost control—by scheduling maintenance and replacing parts before they fail, companies dramatically reduce the chance of costly breakdowns and emergency repairs.
Regulatory changes also drove this evolution. The International Safety Management (ISM) Code made structured, proactive maintenance mandatory for ships on international voyages. ISM Code compliance now hinges on detailed, digital records—proof that every check and repair has been performed. This not only makes audits smoother but also ensures vessels meet global safety standards.
Today, maintenance is planned, scheduled, and documented with digital precision. The benefits go beyond safety and compliance. Research shows that vessels with well-documented maintenance histories can command 10–15% higher resale values, as buyers trust their reliability and efficiency. The industry has moved from reactive firefighting to a culture of foresight, where digital PMS platforms underpin operational reliability, safety, and long-term value.

Safety Nets: How PMS Saves Lives and Bottom Lines
In the world of Maritime Safety, few tools have reshaped daily operations as profoundly as the Planned Maintenance System (PMS). Gone are the days when crews waited for something to break before springing into action. Now, scheduled checks and routine servicing are the norm, replacing crisis repairs with a culture of prevention. This shift is more than just procedural—it’s lifesaving.
Consider the critical systems on board: the main engine, steering gear, fire suppression equipment. These aren’t just boxes to tick; they’re the backbone of vessel performance and safety. Regular, documented maintenance through PMS ensures these systems are checked before problems escalate. As one maritime professional put it:
"A good PMS ensures these safety critical systems are regularly checked and maintained. And crucially, there's proof it was done right."
That proof is not just for peace of mind. It’s a requirement. The ISM Code Compliance—the International Safety Management Code—demands verifiable maintenance records. Without them, a ship risks failing audits, facing port state control detentions, or even being denied permission to sail. In this context, PMS becomes the backbone of Ship Audit Readiness.
Routine checks don’t just tick regulatory boxes. They actively prevent disasters—think steering loss in rough seas or an oil spill from a neglected pipe. Research shows that ships with robust PMS experience fewer critical failures and less unplanned downtime. This translates directly into higher operational reliability and smoother schedules.
There’s also a business case. Every check and repair is logged, creating a transparent maintenance history. Not only does this shorten inspection times in port, but it also boosts the vessel’s resale value—studies indicate that ships with solid PMS can command up to 15% higher prices at sale. Insurers, too, look favorably on well-documented maintenance, often leading to better terms.
Finally, PMS supports smoother crew transitions. With every action recorded, knowledge isn’t lost when hands change. New crew members step aboard with a clear picture of the vessel’s condition, reducing the risk of missed issues and ensuring continuity.
In short, PMS is more than a checklist. It’s a safety net—protecting lives, safeguarding investments, and keeping ships moving safely and efficiently.
The PMS Toolbox: Corrective, Preventive, Predictive
A Planned Maintenance System (PMS) is the backbone of modern vessel reliability, blending multiple maintenance strategies to keep ships running smoothly. At its core, a PMS isn’t just about fixing things when they break—it’s about managing equipment health with structure, foresight, and data. But how do the different approaches fit together?
First, there’s corrective maintenance—the classic “wait until it breaks” method. It’s simple, but the cost of chaos, unplanned downtime, and emergency repairs can be staggering. Corrective action is reactive by nature, often leading to higher expenses and operational headaches. In today’s shipping world, relying solely on this approach is a recipe for trouble.
Stepping up from reactive, preventive maintenance introduces routine checks and scheduled interventions. Think of it like the sticker on your car windshield reminding you when to change the oil. Tasks are planned based on time intervals or usage hours, aiming to catch issues before they escalate. This strategy reduces the risk of sudden breakdowns and extends equipment life, but it can still result in unnecessary part replacements and labor.
Enter predictive maintenance—the cutting edge of maritime maintenance strategies. Here, real-time sensors monitor temperature, vibration, and oil quality. Algorithms analyze this data, detecting subtle signs of wear and forecasting failures before they happen. As one expert puts it:
"Maintenance happens exactly when needed. So it's super optimized, like the machine telling you when it needs attention based on actual condition rather than calendar time."
This approach, often called Condition Based Maintenance (CBM), is gaining traction as sensor technology advances. Research shows that predictive maintenance is more beneficial than preventive maintenance because it targets interventions only when truly necessary, reducing waste and minimizing downtime. Data-driven maintenance strategies use historical and real-time analytics to optimize every task, making ship operations more efficient and cost-effective.
No single method fits every vessel or scenario. A robust Planned Maintenance System blends corrective, preventive, and predictive approaches, adapting to equipment criticality, vessel type, and technology level. The result? A flexible, intelligent framework that keeps ships safer, more reliable, and ready for anything the sea throws their way.
 Inventory Management and the Power of Planning" />
Inventory Management and the Power of Planning" />Invisible Hands: Inventory Management and the Power of Planning
Modern shipping rarely leaves anything to chance, especially when it comes to Inventory Management. At the heart of this transformation are Digital PMS Platforms—systems that quietly but powerfully reshape how vessels manage their spare parts, tools, and consumables. The integration between planned maintenance and inventory is more than a technical upgrade; it’s a shift toward true Operational Efficiency and Cost Control.
Consider the daily reality on board: every maintenance task, from routine inspections to major overhauls, demands the right parts at the right time. With a PMS linked directly to inventory, crews can instantly check spare part availability. No more frantic searches or last-minute calls to shore. As one marine superintendent put it:
"The PMS links directly to inventory systems...triggering reorder requests automatically when supplies run low. That streamlines supply chain and avoids delays from missing parts."
This automation means that spare parts scarcity becomes a rarity. The system tracks consumption as jobs are planned and executed, adjusting stock levels in real time. When a part runs low, automated reorder requests are sent—often before anyone on board even notices. The result? Fewer delays, fewer emergency purchases, and a dramatic reduction in costly rush shipments.
The financial impact is real. There are documented cases where a timely inventory alert helped a vessel avoid a $50,000 rush shipping bill. Multiply that across a fleet, and the savings are substantial. Centralized data also means leaner stock on board, less waste, and more space for what truly matters.
But the benefits don’t stop at cost. Digital PMS Platforms serve as a knowledge base, capturing best practices and maintenance history. This digital record-keeping ensures that even during crew transitions or rough weather, nothing is lost—no more paperwork swept away in a storm. Crews can access procedures and inventory data instantly, reducing mistakes and smoothing handovers.
Ultimately, streamlined inventory management boosts vessel uptime and operational reliability. Research shows that integrating maintenance and inventory systems not only prevents costly delays but also supports compliance, safety, and long-term asset value. The invisible hands of planning and data-driven processes are quietly steering the future of maritime operations.
PMS Puzzles: People, Training, and Tech Hiccups
Digital PMS Platforms have transformed the way vessels approach maintenance, but the journey isn’t always smooth sailing. When it comes to implementing a Planned Maintenance System, technical headaches often surface first. Integration issues between the PMS and other shipboard systems can disrupt workflows, while data security and system compatibility remain constant concerns. With more systems moving to the cloud or networked environments, the stakes are even higher. As one industry expert put it,
"A cyber attack on maintenance system could be devastating. Absolutely. Human side, user resistance due to unfamiliarity or seeing PMS as extra admin work."
Cybersecurity is no longer a theoretical risk. Research shows that maritime systems face a rising number of cyber-attacks each year, though the exact figures remain elusive. The threat is real—imagine a virus halting shipboard repairs in the middle of a storm. To counter these risks, robust cybersecurity measures are essential. Firewalls, encryption, and regular software updates form the backbone of data protection for Digital PMS Platforms. Strong access controls and data validation processes further safeguard Maritime Safety and Operational Efficiency.
Yet, technology is only half the puzzle. Human factors play an equally crucial role in the success of any Planned Maintenance System. Studies indicate that human error or reluctance is a root cause in over 50% of PMS failures or inefficiencies. Crew members may resist new systems, viewing them as extra administrative burdens or simply unfamiliar territory. This resistance can be compounded by a lack of training, leaving teams ill-equipped to leverage the full potential of their maintenance platforms.
The solution? Communication and cultural change. Success hinges on clearly explaining the value of the PMS—how it prevents costly breakdowns, enhances Maritime Safety, and streamlines daily routines. Ongoing training and support are vital, fostering team buy-in and smoother tech adoption. Companies that invest in regular training sessions, transparent change management, and robust backup plans are better equipped to handle system failures or crew errors, ensuring Operational Efficiency even when the unexpected strikes.
Ultimately, adopting a Digital PMS Platform is not just a technical upgrade. It’s a shift in mindset—one that requires both strong technology and a crew ready to embrace change.

Into the Future: AI at the Helm (and in the Engine Room)
The world of ship maintenance is undergoing a quiet revolution. At the heart of this change are next-generation Digital PMS Platforms—systems that are smarter, faster, and more connected than ever before. These platforms are no longer just digital logbooks. Instead, they use Artificial Intelligence and machine learning to analyze millions of data points streaming in from shipboard sensors. The result? A leap forward in Predictive Maintenance and Operational Efficiency.
Imagine a vessel where hundreds of sensors feed real-time data directly into the Planned Maintenance System. As one expert put it:
"Imagine sensors all over ship feeding real time data into PMS automatically. Machine learning algorithms spotting patterns predicting failures well before humans can detect them."
This isn’t science fiction. Research shows that AI-powered PMS can identify subtle warning signs—vibration anomalies, temperature spikes, or pressure drops—long before a human engineer would notice. Problems are fixed before they escalate, maximizing uptime and minimizing costly surprises.
The shift isn’t just about smarter analytics. Cloud-based PMS platforms now enable seamless, real-time data sharing between ship and shore. This means less paperwork, faster decision-making, and improved compliance. Mobile apps let engineers log work on the spot, attach photos, and update records instantly—reducing errors and boosting accountability.
Automation is also transforming compliance and planning. Modern systems generate audit-ready reports automatically, mapping maintenance activities directly to regulatory requirements. Integration with inventory, safety, and voyage planning software creates a unified digital ecosystem, streamlining everything from spare parts management to safety drills.
Yet, as digital PMS platforms become more self-optimizing, a question lingers: can technology ever fully replace the seasoned instincts of experienced engineers? Studies indicate that while AI enhances predictive maintenance and operational reliability, human oversight remains crucial. The most successful systems blend advanced analytics with a culture of teamwork, ongoing training, and clear communication across departments.
Looking ahead, the future of ship maintenance lies in harnessing the full potential of data-driven strategies. Flexible, customizable PMS solutions—backed by robust cybersecurity and strong change management—will define the next era of operational excellence at sea.
Table: Comparing Ship Maintenance Strategies—Old School vs. Digital Genius
When it comes to Maintenance Strategies in the maritime world, the difference between “old school” and “digital genius” is more than just a matter of technology—it’s about operational efficiency, cost control, and safety. Decision-makers today are faced with a spectrum of approaches, from reactive fixes to sophisticated, data-driven systems. The table below offers a quick-glance reference for ship managers, crew, and owners, highlighting the operational, cost, and safety implications of each strategy.
| Strategy | Operational Efficiency | Cost Control | Safety & Risk | Typical Tools/Systems |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corrective (Reactive) | Low—repairs only after failure, high downtime | High costs due to unexpected breakdowns | High risk; safety incidents more likely | Manual logs, ad hoc repairs |
| Preventive (Scheduled) | Moderate—scheduled checks reduce surprises | Moderate costs; some unnecessary maintenance | Lower risk; issues caught early | Planned Maintenance System (PMS), checklists |
| Predictive (Condition-Based) | High—maintenance only when needed, minimal downtime | Optimized costs; avoids over- and under-maintenance | Lowest risk; real-time intervention prevents failures | Digital PMS, sensors, analytics, AI |
Traditional “fix-when-broken” habits—known as corrective maintenance—often lead to high downtime and spiraling costs. Research shows that relying solely on this approach can expose vessels to increased risk and operational disruptions. In contrast, Preventive Maintenance schedules work before failures are expected, much like changing oil based on hours or mileage. This reduces risk and keeps costs moderate, but can still result in unnecessary tasks.
The real leap comes with Predictive Maintenance. Using digital PMS platforms, sensors, and analytics, ships can now monitor equipment in real time—tracking vibration, temperature, and oil quality. Algorithms analyze this data to forecast failures, allowing maintenance to happen exactly when needed. This not only boosts operational efficiency but also delivers superior cost control by minimizing both downtime and unnecessary interventions. For ship owners and managers, the digital approach is quickly becoming the gold standard in planned maintenance systems.
Conclusion: When Routine Wins the Race
In the world of marine engineering, the true brilliance of a Planned Maintenance System (PMS) isn’t just in its digital dashboards or predictive analytics. It’s in the quiet, relentless routine that keeps ships running safely and efficiently. As research shows, the shift from reactive repairs to proactive maintenance is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity for operational efficiency and compliance with maritime standards. The benefits of planned maintenance extend far beyond machinery; they touch every aspect of shipboard life, from safety and risk management to crew morale and cost control.
Yet, technology alone doesn’t guarantee success. The heart of any effective Planned Maintenance System lies in the people who use it. As one industry veteran put it,
"Commitment to systematic work, documentation, and teamwork is crucial."This commitment is what transforms a set of digital tools into a living, breathing safety net. Smart maintenance is as much about fostering a culture of diligence and accountability as it is about leveraging the latest software. The best systems blend tradition with innovation—think of the retired chief engineer’s logbook, its pages worn and dog-eared, now scanned and referenced via a mobile app by the next generation of seafarers.
The industry trend is clear: digital PMS platforms are steadily expanding into every corner of ship operations. But future-proofing these systems means more than just adopting new tech. It requires flexibility—choosing solutions that can be customized and integrated, investing in cybersecurity, and prioritizing crew training. Unlocking the full power of data is key, but so is ensuring that human judgment remains at the helm. After all, even the most advanced predictive maintenance algorithms can’t replace the seasoned intuition of a crew member who knows when something just feels off.
Ultimately, the greatest planned maintenance benefits come from a balanced approach. Operational reliability and safety are achieved not just through automation, but through a culture that values routine, documentation, and the timeless wisdom of “better safe than sorry.” In marine engineering, as in life at sea, it’s the steady hand and the well-worn checklist that often win the race.
TL;DR: Modern, tech-driven planned maintenance is the backbone of smooth, safe shipping. By moving from frantic fixes to proactive, predictive systems, ships save money, avoid disaster, and keep global trade afloat—all thanks to a quiet revolution below deck.

Comments
Post a Comment