Imagine having X-ray vision to see potential problems before they become serious issues—this is the magic of infrared thermography. Join us as we delve into this cutting-edge technology that offers shipyard professionals a means of safeguarding their operations and significantly cutting costs. With stories from industry insiders, you’ll learn about its fascinating applications and hear about real-world savings that could change your approach to maintenance.
The Basics of Infrared Thermography: What You Need to Know
Definition and Explanation of Infrared Thermography
Infrared thermography is a powerful technology that allows individuals to "see" heat. Imagine having x-ray vision, but instead of seeing bones, you see heat patterns. This method uses thermal cameras to detect infrared radiation emitted by objects. Every object, regardless of its state, emits some level of infrared energy based on its temperature. By capturing this energy, thermography provides a visual representation of heat patterns, known as thermograms.
The Science of Infrared Radiation and Thermograms
At the heart of infrared thermography lies the science of infrared radiation. This type of radiation is invisible to the naked eye but is emitted by all objects. When an object heats up, it emits more infrared radiation. Thermal cameras are designed to detect this radiation and convert it into visible images. These images, or thermograms, showcase temperature variations across surfaces, helping to identify issues that might not be visible through standard visual inspection.
Comparison of Visual Inspection vs. Thermal Imaging
When it comes to inspecting systems, traditional visual inspection has its limitations. A technician may look at a machine and see nothing wrong. However, underlying issues, like overheating components or electrical faults, often remain hidden. This is where thermal imaging shines. It can reveal problems that are otherwise invisible.
- Visual Inspection: Relies on the technician's ability to see and interpret what is visible.
- Thermal Imaging: Provides a detailed thermal map, highlighting temperature differences that indicate potential issues.
As an expert once said,
“Thermography allows us to visualize potential issues that are otherwise hidden, enabling critical preventative maintenance.”
How Thermal Cameras Work: Transforming Heat into Visible Data
Thermal cameras work by detecting infrared radiation and converting it into a visual format. The process involves several steps:
- Detection: The camera's sensor detects infrared radiation emitted by objects.
- Conversion: This radiation is converted into an electrical signal.
- Image Creation: The signal is processed to create a thermogram, displaying temperature variations.
These thermograms are invaluable in various applications, from industrial settings to building inspections. For instance, in shipyards, thermal imaging can identify overheating electrical components, plumbing leaks, and even structural issues in ship hulls.
Importance of Understanding Infrared Radiation in Everyday Applications
Understanding infrared radiation is crucial not only in industrial settings but also in everyday applications. For example, in HVAC systems, thermography can help identify inefficiencies, leading to better energy management. In buildings, it can detect insulation failures or moisture intrusion, which can save homeowners significant repair costs.
Applications of Thermography Beyond Shipyards
While shipyards are a primary application area for infrared thermography, its uses extend far beyond. Here are a few examples:
- Building Inspections: Identifying heat loss or moisture issues.
- Electrical Inspections: Spotting overheating components in electrical panels.
- Mechanical Systems: Detecting underlubrication in motors and pumps.
In each case, the ability to visualize heat patterns leads to proactive maintenance and significant cost savings.
Infrared thermography is a remarkable tool that enhances safety and efficiency across various industries. By understanding how it works and its applications, individuals can leverage this technology to prevent costly breakdowns and improve operational performance.
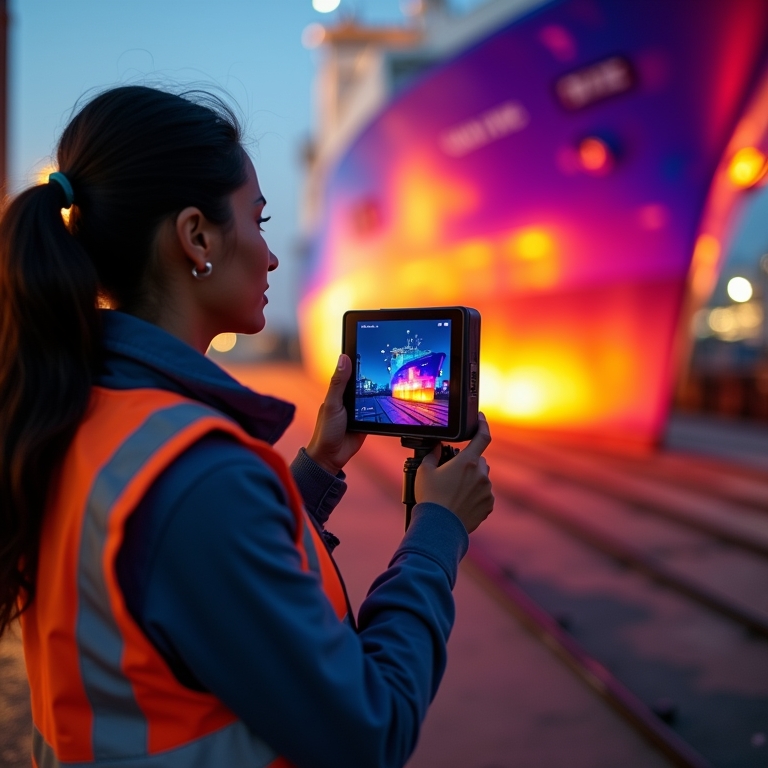

Practical Applications of Infrared Thermography in Shipyards
Infrared thermography is a powerful tool in shipyards, offering numerous practical applications. This technology allows professionals to visualize heat patterns, which can reveal potential issues in various systems. Here are some key areas where infrared thermography proves invaluable:
1. Detecting Overheating in Electrical Systems
Electrical systems are critical for the operation of any ship. Overheating components can lead to significant failures. Infrared thermography can identify these hot spots before they escalate into serious problems. Imagine a ship's electrical panel where a connection is loose. This can generate excess heat, which, if left unchecked, might result in a catastrophic failure. By using thermal cameras, technicians can spot these issues early.
2. Maintenance Benefits for Mechanical Components
Mechanical components like motors and pumps are essential for a ship's functionality. Regular maintenance is crucial to avoid breakdowns. Infrared thermography helps in identifying problems such as:
- Underlubrication of bearings
- Steam leaks in pumps
By detecting these issues early, shipyards can schedule maintenance before a failure occurs. This proactive approach not only saves money but also ensures operational efficiency.
3. Assessing Ship Hull Integrity
The integrity of a ship's hull is paramount. Delamination in materials can lead to leaks or even structural failures. Infrared thermography can assess the condition of the hull without invasive methods. By identifying areas of concern, shipyards can address potential issues before they become critical.
4. Evaluating Plumbing Systems for Leaks
Leaks in plumbing systems can cause extensive damage if not detected early. Thermal imaging can quickly identify these leaks by revealing temperature differences in the plumbing. This allows for targeted repairs, minimizing disruption and cost.
Significant Savings Through Early Detection
Utilizing infrared thermography can lead to substantial savings. For instance, a report indicated potential savings of $77,000 through early detection of faults. This figure highlights the financial benefits of implementing thermal imaging in routine inspections.
Real-World Examples
There are numerous real-world examples of cost reductions achieved through thermography. For instance, companies have reported significant savings in ship insulation inspections. By identifying thermal inefficiencies, they can make informed decisions about repairs and upgrades. This not only enhances safety but also improves energy efficiency.
“Early detection through thermography can save companies thousands in unanticipated repairs.” – [Expert Name]
The Versatility of Thermal Imaging
Thermal imaging is not limited to just one area of ship maintenance. Its versatility allows it to pinpoint various issues, from overheating to leaks. This makes it an invaluable asset for shipyards looking to enhance their maintenance protocols.
In conclusion, infrared thermography is a game-changer in shipyards. By detecting overheating in electrical systems, maintaining mechanical components, assessing hull integrity, and evaluating plumbing systems, it provides a comprehensive approach to ship maintenance. The potential for significant savings further emphasizes its importance in the industry.
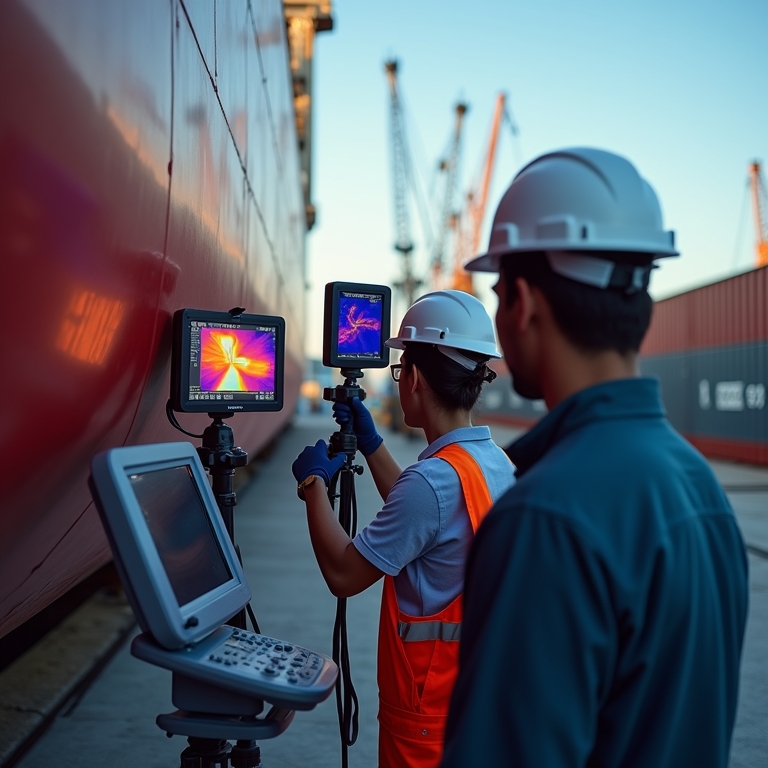

The Importance of Regular Inspections and Expertise in Thermography
In the world of industrial maintenance, infrared thermography is a game changer. It allows professionals to visualize heat patterns, helping to identify potential issues before they escalate. This is especially crucial in environments like shipyards, where machinery operates under demanding conditions. Regular inspections are not just a good practice; they are essential for maintaining equipment health.
Frequency of Thermal Scans
The Hartford Steam Boiler (HSB) recommends that companies conduct full infrared scans every three years for standard equipment. But what about critical machinery? In harsh environments like shipyards, more frequent evaluations are advisable. Why? Because the stakes are higher. A malfunctioning component can lead to costly repairs or even accidents.
- Every three years: This is the baseline for standard equipment.
- More frequent scans: Necessary for critical machinery in challenging conditions.
Regular inspections ensure ongoing equipment health. This is imperative in a shipyard's demanding environment. After all, a small issue can snowball into a major problem if left unchecked.
The Role of Qualified Personnel
Having the right technology is only part of the equation. The real value lies in the expertise of the personnel interpreting the thermal images. Infrared thermography is not just about capturing images; it’s about understanding what those images mean. This requires training and experience.
As one expert aptly stated,
The value of infrared inspections lies not just in the technology itself, but in the expertise behind it.This highlights the need for qualified personnel who can accurately interpret the data.
Certifications for Thermography Professionals
To ensure that personnel are adequately trained, various certifications are available. These range from Level I to Level III, each emphasizing different levels of expertise. For instance:
- Level I: Basic understanding of thermography principles.
- Level II: Intermediate skills, including image analysis.
- Level III: Advanced knowledge, capable of overseeing thermography programs.
These certifications are crucial for anyone looking to advance their knowledge in thermography practices. They ensure that personnel are equipped to handle the complexities of thermal imaging.
Innovations in Thermography: Iris Inspection Windows
Technological advancements have also made inspections safer and more efficient. Innovations like Iris inspection windows allow for easier access during inspections. This means technicians can perform checks without having to open panels or interact directly with live wires. Such innovations significantly reduce risk, making the inspection process smoother and safer.
In summary, regular inspections and the expertise of qualified personnel are vital for effective thermography. The HSB recommendations provide a solid foundation for maintenance schedules, while certifications ensure that personnel are well-equipped to interpret thermal images accurately. Innovations like Iris inspection windows further enhance safety and efficiency in inspections. In the demanding environment of a shipyard, these elements work together to prevent costly breakdowns and ensure operational continuity.
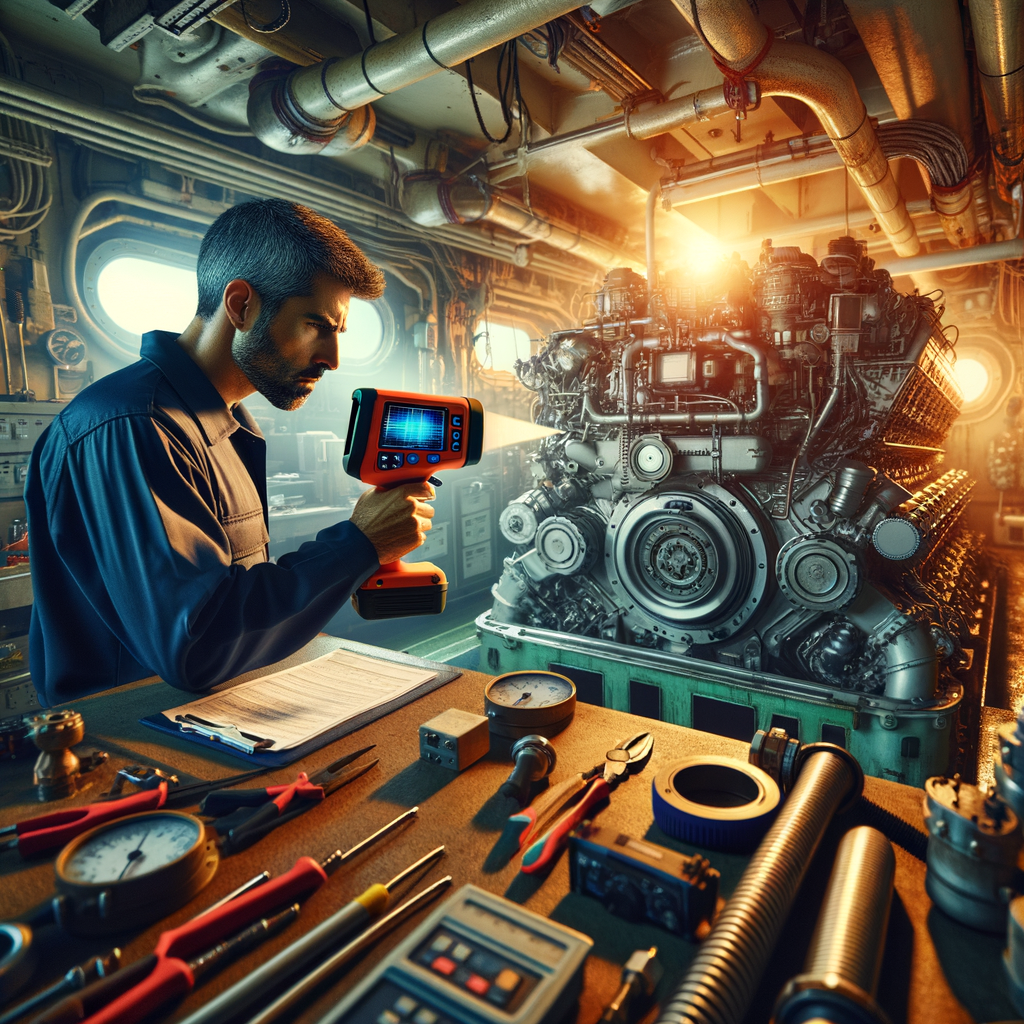

Selecting the Right Thermal Imaging Equipment for Your Needs
Choosing the right thermal imaging equipment can seem daunting. With various options available, it's essential to understand the key factors that influence your decision. This guide will help clarify those factors, ensuring you select the best equipment for your specific needs.
1. Understanding Detector Types: Cooled vs. Uncooled
One of the first decisions to make involves the type of detector in the thermal camera. There are two primary types: cooled and uncooled.
- Cooled detectors are more sensitive and provide better image quality. They require a cooling mechanism, which can make them bulkier and more expensive.
- Uncooled detectors are more common and user-friendly. They are typically smaller, lighter, and less expensive, making them suitable for many applications.
When deciding between the two, consider the specific requirements of your work. Will you need high sensitivity, or is portability more critical? This choice can significantly impact your thermography results.
2. Choosing Cameras Based on Resolution and Thermal Sensitivity
Resolution and thermal sensitivity are crucial factors in selecting a thermal camera. Resolution refers to the clarity of the thermal image, while thermal sensitivity indicates the camera's ability to detect small temperature differences.
- Higher resolution cameras provide clearer images, making it easier to identify issues.
- Thermal sensitivity is measured in milliKelvins (mK). A lower mK value means the camera can detect smaller temperature variations.
For example, if a technician is inspecting electrical panels, a camera with high resolution and sensitivity can help pinpoint overheating components that might otherwise go unnoticed. As the saying goes,
“Not all thermal cameras are created equal; choosing the right one is essential for accurate diagnostics.” – [Expert Name]
3. Evaluating Temperature Ranges
Different applications require different temperature ranges. Some cameras can measure temperatures from -20°C to 1200°C, while others may only cover a narrower range.
When evaluating temperature ranges, consider the environments you will be working in:
- Will you be inspecting electrical systems that operate at lower temperatures?
- Or will you need to assess high-temperature machinery?
Understanding the temperature range you need will help you avoid purchasing a camera that is either too limited or overly complex for your requirements.
4. Assessing Features That Enhance Usability in the Field
Usability is another critical aspect when selecting thermal imaging equipment. Some features can significantly enhance the user experience:
- Lightweight design makes it easier to carry during inspections.
- Durability ensures the camera can withstand harsh environments.
- Intuitive interfaces simplify operation, allowing technicians to focus on the task rather than struggling with the equipment.
Additionally, consider features like built-in Wi-Fi for easy data transfer and storage. These can streamline the inspection process and improve efficiency.
5. The Importance of Quality Equipment
Investing in quality thermal imaging equipment is crucial for effective thermography. High-quality cameras can lead to better diagnostics, ultimately saving time and money. Specific features may be more beneficial for various industrial contexts, so it's essential to tailor your selection to your unique needs.
In conclusion, selecting the right thermal imaging equipment involves understanding detector types, resolution, temperature ranges, and usability features. By carefully considering these factors, one can ensure they choose the best thermal camera for their specific applications. After all, the right choice can make all the difference in identifying potential issues before they escalate into costly problems.
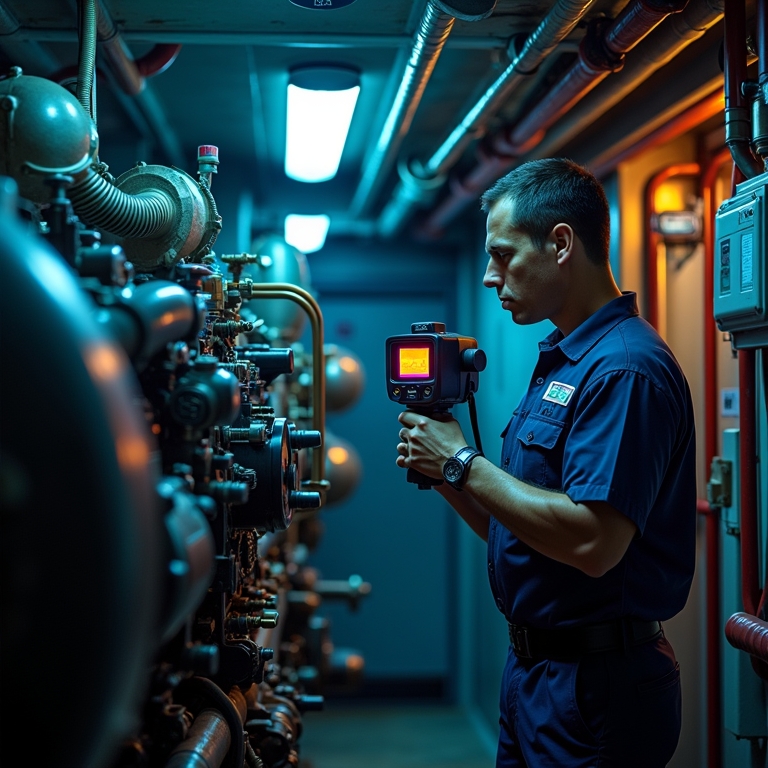 Preventive Maintenance in Shipyards Through Thermography" />
Preventive Maintenance in Shipyards Through Thermography" />Conclusion: The Future of Preventive Maintenance in Shipyards Through Thermography
As the maritime industry continues to evolve, the importance of thermography in shipyards cannot be overstated. This innovative technology allows for the visualization of heat patterns, enabling the detection of potential issues that may otherwise go unnoticed. By utilizing thermal cameras, shipyards can identify problems in electrical and mechanical systems, which is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency.
Key Insights About Thermography
Thermography is often likened to having x-ray vision for thermal energy. It provides a unique perspective on the health of various systems. For instance, it can detect overheating components, loose connections, and even plumbing leaks. The versatility of thermal imaging extends to assessing the integrity of ship hulls and spotting electrical infrastructure issues. However, it is essential to note that interpreting these thermal images requires a certain level of expertise.
The Financial Rationale Behind Preventative Maintenance Initiatives
Investing in preventive maintenance through thermography can lead to significant financial savings. According to reports from HSB, early detection of issues can save companies tens of thousands of dollars. For example, identifying an overheated transformer can prevent costly repairs, as evidenced by a case where a company saved around $77,000 by addressing the problem early. This financial rationale underscores the importance of adopting thermography as a standard practice in shipyards.
Embracing Evolving Inspection Technologies
The landscape of inspection technologies is constantly changing. Shipyards must embrace these advancements to stay competitive. Innovations like Iris inspection windows enhance safety by allowing easier access during inspections without risking exposure to live wires. This evolution not only improves safety protocols but also promotes a culture of proactive maintenance. As the industry moves forward, it is vital for professionals to stay informed about new technologies and their applications.
Safety and Efficiency Benefits for Shipyards
Ultimately, the integration of thermography into maintenance strategies leads to improved safety and efficiency in shipyards. Regular inspections can identify potential failures before they escalate into costly downtime. The ability to detect issues such as underlubrication or steam leaks early on is critical in preventing operational disruptions. Moreover, the safety of personnel is enhanced when potential hazards are identified and addressed promptly.
To summarize, thermography is a powerful tool that offers numerous benefits for shipyards. It not only aids in identifying potential issues but also provides a solid financial rationale for preventive maintenance initiatives. As the technology continues to evolve, embracing these advancements will be crucial for maintaining safety and efficiency in shipyard environments.
“Investing in technology and training today ensures operational success tomorrow.” – [Expert Name]
In conclusion, the utilization of thermal imaging can pave the way for smarter maintenance strategies. By integrating innovation and training into their operations, shipyards can significantly enhance their safety protocols and operational efficiency. The future of preventive maintenance lies in the hands of those who are willing to adapt and embrace these evolving technologies.
TL;DR: Infrared thermography is essential for recognizing heating issues in shipyard systems, preventing significant failures and saving costs through early detection. Emphasis on expertise and regular inspections promotes safety and efficiency in challenging environments.
Comments
Post a Comment